Market Penetration Strategy 101: How to Calculate & Best Strategies

Market penetration can elevate a business to new levels by tapping into existing products in current markets. This article will delve into what market penetration is, how it’s calculated, and the optimal strategies to achieve it. Whether you’re a startup or an established enterprise, understanding market penetration can help enhance market share and drive success.
What is Market Penetration?
Market penetration is a business growth strategy where companies aim to increase their market share of existing products or services in existing markets. Market penetration is crucial for businesses looking to solidify their presence in an industry and build a robust customer base.
This is done by selling more products or services to current customers or by finding new customers within existing markets. It can be achieved through various tactics like pricing strategies, advertising, sales promotions, and product improvements or innovations. The primary goal of this strategy is to increase market share, revenue, and customer loyalty within a market where the products or services are already available.
The degree of market penetration can be an indicator of the brand’s popularity, business growth, and the level of risk involved. It’s crucial for evaluating the success of products and services in the market and is also a critical factor in developing effective marketing strategies and plans.

How is Market Penetration Calculated?

Market Penetration is calculated to understand the existing sales or market share of a company in comparison to the total market potential. It provides insights into how much of the potential market a company has been able to capture.
Formula for Market Penetration Rate
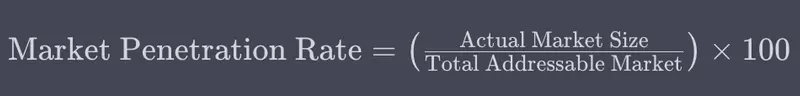
Actual Market Size is the current market share or sales volume of the company.
Total Addressable Market (TAM) represents the total sales revenue opportunity available for all companies in a particular market.
Example:
Let’s say a company sells 500 units annually in a market where 10,000 units are sold in total by all competitors. The Market Penetration Rate would be:
This calculation implies that the company has captured 5% of the total market.
Additional resources:
- Total Addressable Market Template– In order to help calculate your market share and your potential to build a large business, it helps to calculate and understand the total addressable market and sensitivity analysis. Check out our free total addressable market template below
- When & How to Calculate Market Share (With Formulas)
Suggest Market Penetration Rate for Startups
Once you’ve calculated the market penetration rate, it’s essential to analyze it in context. A high rate may indicate a strong market presence but may also suggest market saturation, limiting growth. A lower rate can point to significant growth opportunities, but it could also reflect poor market fit or strong competition.
Companies often use market penetration metrics alongside other market analysis tools and industry benchmarks to develop effective market strategies and identify growth opportunities.
For startups, achieving a market penetration rate of 2-3% is often considered commendable, and it can serve as a strong foundation for further expansion and growth.
8 Best Market Penetration Strategies
To achieve greater market penetration, various strategies can be implemented. The selection depends on the business model, industry, and target audience. Below are eight effective market penetration strategies:
1) Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic Pricing can be a powerful tool for companies looking to penetrate existing markets more deeply. It is a strategy where companies adjust the prices of their products or services in real-time, or near real-time, in response to market demands, competitor prices, and other external factors.
This strategy can be pivotal in achieving higher market share in existing markets as it allows businesses to quickly adapt to market conditions and customer behaviors.
By adjusting prices to meet market conditions and consumer expectations, businesses can optimize their sales and profits, attract more customers, and enhance their market share. However, it’s crucial to manage this strategy carefully to maintain customer trust and satisfaction.
How It Works:
Dynamic Pricing leverages advanced technologies and algorithms to analyze multiple factors that influence demand, including seasonality, competitor prices, inventory levels, and consumer behavior. Based on this analysis, prices are adjusted to optimize sales, revenue, or margins.
Pros
- Maximizes Revenue: Enables businesses to adjust prices to meet demand, maximizing revenue during high demand and possibly stimulating sales during low demand.
- Competitive Advantage: Allows for real-time response to competitors’ pricing strategies, helping companies stay competitive in the market.
- Optimizes Inventory: Helps in managing inventory more effectively by increasing prices when stock is low or decreasing prices to move surplus inventory.
- Customer Segmentation: Offers the possibility to segment customers and offer different prices based on customer willingness to pay, optimizing revenue and customer satisfaction.
- Market Responsiveness: Provides the flexibility to quickly respond to market conditions like changes in demand or supply, ensuring optimal pricing at all times.
Cons
- Customer Dissatisfaction: Customers may perceive dynamic pricing as unfair, especially if they find out they paid more for the same product or service than others, potentially leading to loss of trust and customer churn.
- Complex Implementation: Requires sophisticated software, algorithms, and expertise to analyze data and adjust prices accurately and effectively, which can be resource-intensive.
- Brand Image Risk: Frequent price changes, especially upward revisions, can lead to a negative brand image and accusations of price gouging.
- Price Wars: Can lead to destructive price wars with competitors, resulting in decreased profit margins for all market players.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: In some industries and jurisdictions, there may be legal restrictions and ethical considerations around dynamic pricing, and violating these can lead to fines and reputational damage.
2) Adding Distribution Channels
Adding distribution channels refers to the strategy of increasing the number of ways or locations through which customers can access and purchase a company’s products or services.
By making products or services available through a variety of channels, companies can reach a broader audience, adapt to customer purchasing preferences, and ultimately increase sales and market share within existing markets. This strategy requires careful planning and management to ensure consistency in brand image and customer experience across all channels.
Pros
- Increased Sales: Access to more customers through varied channels can lead to higher sales and subsequently, increased market share.
- Enhanced Market Coverage: More channels mean broader market coverage, enabling the business to reach different customer segments and geographic locations within the existing market.
- Customer Convenience: Providing multiple purchasing options caters to diverse customer preferences, potentially improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Risk Diversification: Distributing through various channels reduces dependency on one, mitigating risks associated with the underperformance of a single channel.
- Brand Visibility: Presence across multiple channels enhances brand visibility and awareness, contributing to brand equity.
Cons
- Complex Management: Managing multiple channels can be logistically complex and administratively challenging, requiring additional resources and efforts.
- Inconsistent Brand Image: Maintaining a consistent brand image and customer experience across varied channels can be challenging, potentially affecting brand perception.
- Channel Conflict: Different channels might compete against each other for the same customers, leading to potential conflicts and affecting relationships with channel partners.
- Reduced Profit Margins: Some channels might require price reductions or additional expenditures, such as commissions for third-party sellers, impacting profit margins.
- Customer Confusion: Offering products through too many channels, especially with varied pricing or promotional offers, can confuse customers and dilute the brand value.
When adding distribution channels, companies need to strategically assess the potential impact on the brand, customer experience, and overall business operations. Proper integration, management, and consistent monitoring of all channels are crucial to addressing the challenges and reaping the benefits of this strategy. Balancing the added complexity with the potential advantages is key to successful implementation and sustainable growth in market penetration.
3) Geo-Targeting Specific Locations
Geo-targeting specific locations involves tailoring your marketing and sales efforts to target customers in a specific geographical area or region. This technique is often utilized by businesses to focus resources on areas where they are likely to gain the most traction, allowing them to reach and serve customers more effectively and efficiently.
Geo-targeting can be implemented using various tools and platforms like online advertising services, SEO, and social media, which allow businesses to specify the geographic locations they want to target. Additionally, analytics and data analysis can help in identifying the most lucrative regions to focus on.
Pros
- Enhanced Personalization: Allows for more personalized and locally relevant marketing campaigns, improving engagement and conversion rates.
- Resource Optimization: Focuses resources and efforts on high-potential or high-performing regions, ensuring better utilization and improved ROI.
- Improved Customer Experience: Offering localized content, deals, and products caters to regional preferences and needs, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Market Insight: Provides valuable insights into regional market trends, consumer behavior, and preferences, aiding in better decision-making and strategy formulation.
- Competitive Edge: Establishing a strong presence in specific locations can provide a competitive advantage, especially in areas with less competition.
Cons
- Limited Reach: Focusing on specific locations might limit the overall reach of the business, potentially missing out on opportunities in other regions.
- Resource Intensity: Developing localized strategies and content can be resource-intensive and might require significant investment in research and adaptation.
- Market Variability: Different regions may exhibit varying demand patterns, requiring constant adjustments and refinements to the targeting strategy.
- Cultural Sensitivity: There’s a risk of misunderstanding local cultures and preferences, which might lead to ineffective or even offensive campaigns.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The use of location data can raise privacy concerns and regulatory issues, potentially leading to legal challenges and reputational damage.
4) Continuous Improvements of Products
Continuous improvements of products refer to the ongoing effort to refine and enhance products based on customer feedback, market demands, technological advancements, or competitive dynamics. This strategy is crucial in market penetration as it helps in maintaining and enhancing the appeal of the products, addressing evolving customer needs, and staying competitive in the market.
Pros
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Addressing customer needs and resolving issues lead to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhanced Market Position: Ongoing improvements help in maintaining a competitive edge and solidifying market presence.
- Revenue Growth: Enhanced features and quality can justify higher pricing, leading to increased revenue.
- Brand Strengthening: Demonstrating commitment to excellence and innovation enhances brand reputation and equity.
Cons
- High Costs: Constant refinement and development can be resource-intensive and costly.
- Overcomplication: Adding too many features or making too many changes can complicate the product, potentially alienating users.
- Customer Overwhelm: Frequent changes and updates can overwhelm and frustrate customers, especially if they are not well-communicated.
- Market Misalignment: Without proper market research, improvements may not align with actual customer needs, leading to wasted resources and missed opportunities.
5) Launch a New Product or Rebrand
Launching a new product or rebranding refers to the introduction of a novel product or a significant transformation of existing brand elements, respectively, to appeal to the current market. This can be a pivotal market penetration strategy, aiming to renew consumer interest and address evolving market demands, preferences, and competition.
Pros
- Increased Market Share: New or revitalized offerings can attract a wider audience and capture additional market segments.
- Enhanced Brand Image: A successful rebrand can modernize and elevate the brand’s image, improving perceptions and attractiveness.
- Revenue Growth: New products and improved brand image can drive sales and potentially allow for premium pricing.
- Adaptation to Market Changes: Enables the business to stay relevant and responsive to evolving market trends, demands, and consumer expectations.
Cons
- High Risk and Uncertainty: The success of a new product or a rebrand is not guaranteed and may not resonate with consumers, leading to financial losses.
- Substantial Investment: Development, launch, and rebranding processes can be costly, involving substantial investment in research, marketing, and implementation.
- Potential Customer Alienation: Existing customers may react negatively to significant changes in products or brand identity, potentially leading to loss of loyalty.
- Implementation Challenges: Executing a rebrand or launching a new product involves logistical, operational, and strategic challenges, requiring meticulous planning and coordination.
6) Build Relationships With Business Partners
Building relationships with business partners involves creating and nurturing mutually beneficial connections with other businesses, suppliers, distributors, or stakeholders in your industry. This strategy is crucial in market penetration as it can open up new avenues for growth, co-development, and expansion, allowing businesses to leverage collective resources, networks, and expertise to enhance market presence.
Pros
- Expanded Reach: Access to partners’ networks and resources can significantly extend market reach and presence.
- Increased Innovation: Collaborative efforts can lead to innovative solutions and offerings, enhancing competitive advantage.
- Cost Efficiency: Sharing resources and responsibilities can lead to reduced operational costs and increased efficiency.
- Enhanced Learning: Exposure to partners’ expertise and insights can lead to valuable learning and growth opportunities.
Cons
- Potential Conflicts: Divergent goals, values, or management styles can lead to conflicts and strains in partnerships.
- Dependence Risks: Reliance on partners can pose risks in case of disagreements, underperformance, or termination of partnerships.
- Loss of Control: Collaborations may require concessions and shared decision-making, potentially leading to loss of control over certain aspects of the business.
- Resource Diversion: Managing partnerships can be resource-intensive and might divert focus and resources from core activities.
7) Buy a Smaller Competitor in Your Industry
Buying a smaller competitor, also known as acquisition, refers to purchasing another company to control its assets and operations. This market penetration strategy can be powerful, as it allows a company to quickly increase its market share, expand its product or service offerings, and eliminate competition.
When considering acquiring a smaller competitor, thorough due diligence is paramount to assess the compatibility, valuation, and potential synergies accurately. A well-planned integration strategy, clear communication, and cultural alignment are crucial for realizing the full benefits of the acquisition and ensuring smooth transition and consolidation, thus enhancing market penetration and long-term success.
Pros
- Rapid Market Expansion: Provides immediate access to new market segments, geographic areas, and customer groups.
- Enhanced Resources and Technologies: Acquisition brings in additional resources, technologies, and intellectual properties, enhancing overall capabilities.
- Cost and Revenue Synergies: Merging operations can lead to cost savings and additional revenue opportunities, increasing profitability.
- Strategic Positioning: Reducing competition and leveraging combined strengths can strengthen market positioning and dominance.
Cons
- Integration Challenges: Merging different corporate cultures, systems, and operations can be complex and challenging.
- High Costs and Risks: Acquisition involves significant financial investment and carries risks of overvaluation and unanticipated complications.
- Potential Culture Clash: Differences in organizational cultures and management styles can lead to conflicts and employee dissatisfaction.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Acquisitions may be subject to stringent regulatory scrutiny and approval, potentially impacting the feasibility and timelines.
8) Provide a Rewards Program or Promotional Program
Providing a Rewards or Promotional Program refers to offering incentives like discounts, points, or special offers to customers to encourage loyalty, repeat business, and attract new customers. These programs are instrumental in market penetration as they help in increasing product or service usage among existing customers and drawing in new clientele.
When implementing rewards or promotional programs, it is important to balance the incentives with the overall business strategy and ensure that the programs are sustainable, beneficial, and aligned with brand values. A well-crafted and managed rewards program can be a powerful tool for market penetration, building long-lasting relationships with customers, and creating a competitive advantage in the market.
Pros
- Increased Sales: By incentivizing purchases, such programs can drive up sales volumes and revenues.
- Customer Data Collection: These programs often involve collecting customer data, which can be analyzed to gain insights into consumer behavior and preferences.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Customers receiving rewards or benefits are likely to be more satisfied and have a positive perception of the brand.
- Effective Word-of-Mouth Marketing: Satisfied customers, especially those benefiting from rewards, are more likely to recommend the brand to others.
Cons
- Cost Implications: Implementing and maintaining rewards programs can be costly, impacting profit margins.
- Customer Expectation Management: Customers may come to expect regular promotions, potentially impacting perceived value and full-price sales.
- Complexity in Management: Designing, managing, and optimizing rewards or promotional programs can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Risk of Decreased Perceived Value: Regular and extensive promotions can lead to a devaluation of the product or service in the eyes of consumers.
Raise Funds and Penetrate Your Market With Visible

Market penetration is a pivotal strategy for businesses aiming to enhance their market share in existing markets with existing or innovative products. Whether it’s through employing dynamic pricing, adding distribution channels, geo-targeting, continually improving products, launching new products or rebranding, forging business partnerships, acquiring smaller competitors, or providing compelling rewards or promotional programs, each strategy carries its unique set of advantages and challenges.
The key is to meticulously analyze and integrate these strategies, aligning them with the overarching business objectives, customer needs, and market dynamics, to drive sustainable growth and success. Leveraging such multifaceted approaches can aid in navigating the competitive landscape, fostering customer loyalty, and achieving a robust market presence, propelling your business to new heights. And, to successfully penetrate the market, raising funds effectively is crucial—discover how Visible can assist in making your fundraising journey seamless and successful.
Related resource: What is Internal Rate of Return (IRR) in Venture Capital